ERC-7857: Technical Standard
Overview
ERC-7857 extends ERC-721 to support encrypted metadata, specifically designed for tokenizing AI agents and sensitive digital assets.
- Understanding of ERC-721 NFT standard
- Basic cryptography knowledge (encryption, hashing)
- Smart contract development experience
- Familiarity with oracle systems
Document Purpose
This page provides the technical specification, implementation details, and security considerations for ERC-7857. For high-level concepts, see the INFT Overview.
Key Technical Features
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Encrypted Metadata | Store sensitive data securely | Protects proprietary AI models |
| Secure Re-encryption | Transfer without data exposure | Maintains privacy during ownership changes |
| Oracle Verification | TEE/ZKP proof validation | Ensures transfer integrity |
| Authorized Usage | Grant access without ownership | Enables AI-as-a-Service models |
Technical Specification
Core Interface
interface IERC7857 is IERC721 {
// Transfer with metadata re-encryption
function transfer(
address from,
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
bytes calldata sealedKey,
bytes calldata proof
) external;
// Clone token with same metadata
function clone(
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
bytes calldata sealedKey,
bytes calldata proof
) external returns (uint256 newTokenId);
// Authorize usage without revealing data
function authorizeUsage(
uint256 tokenId,
address executor,
bytes calldata permissions
) external;
}
Transfer Architecture
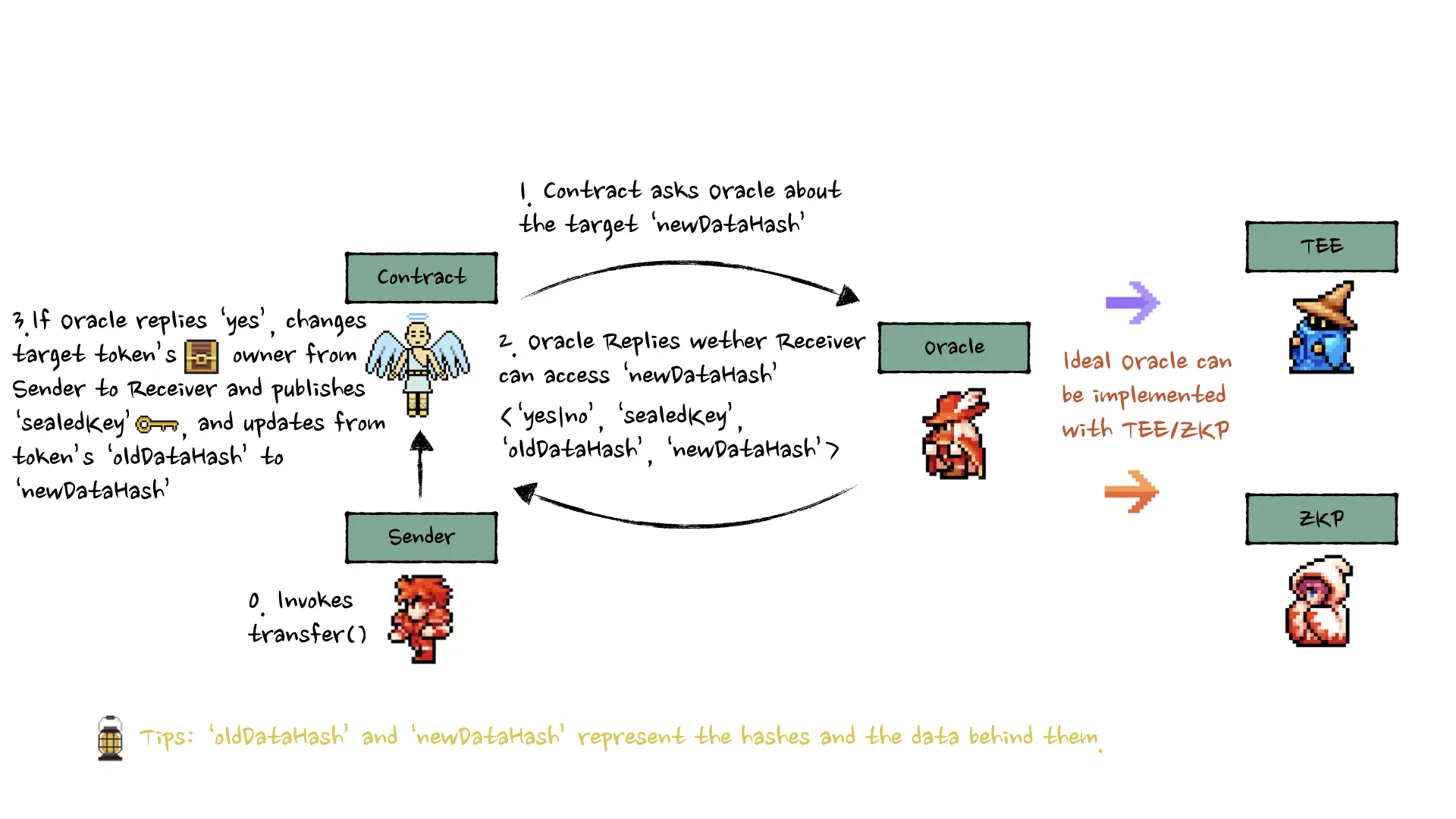
Security Guarantees:
✅ Metadata remains encrypted throughout process
✅ Only new owner can decrypt transferred data
✅ Transfer integrity cryptographically verified
✅ No intermediary can access sensitive information
Oracle Implementations
ERC-7857 supports two oracle types for secure metadata re-encryption:
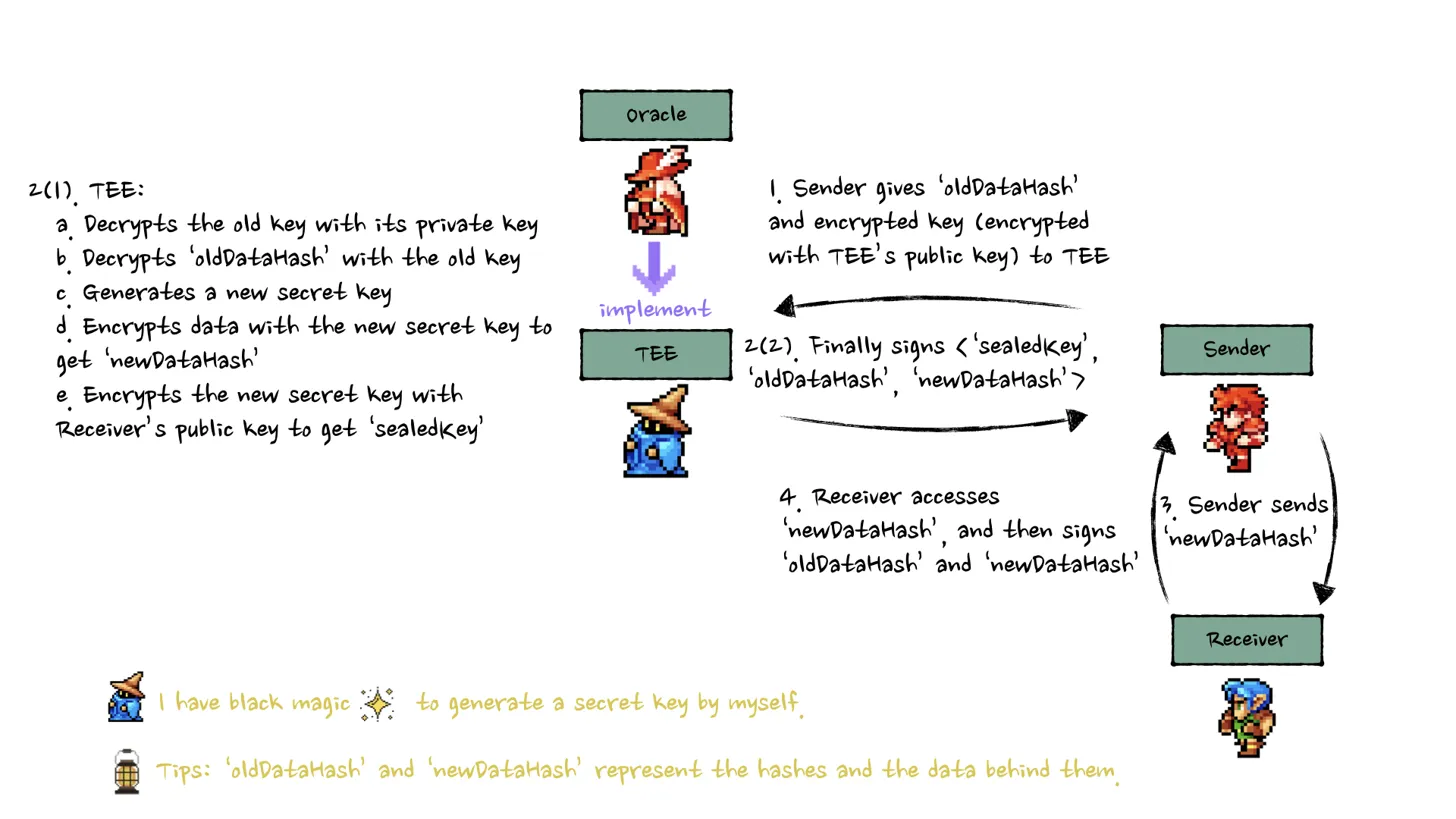
TEE (Trusted Execution Environment)
How it works:
- Sender transmits encrypted data + key to TEE
- TEE securely decrypts data in isolated environment
- TEE generates new key and re-encrypts metadata
- TEE encrypts new key with receiver's public key
- TEE outputs sealed key and hash values
Advantages:
- Hardware-level security guarantees
- TEE can generate cryptographically secure keys
- Attestation provides proof of secure execution
TEE Implementation Example
class TEEOracle {
async processTransfer(encryptedData, oldKey, receiverPublicKey) {
// All operations happen inside secure enclave
try {
// Step 1: Decrypt original data
const data = await this.decryptSecurely(encryptedData, oldKey);
// Step 2: Generate new encryption key
const newKey = await this.generateSecureKey();
// Step 3: Re-encrypt with new key
const newEncryptedData = await this.encryptSecurely(data, newKey);
// Step 4: Seal key for receiver
const sealedKey = await this.sealForReceiver(newKey, receiverPublicKey);
// Step 5: Generate attestation proof
const proof = await this.generateAttestation({
originalHash: hash(encryptedData),
newHash: hash(newEncryptedData),
receiverKey: receiverPublicKey
});
return {
newEncryptedData,
sealedKey,
proof
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`TEE processing failed: ${error.message}`);
}
}
}
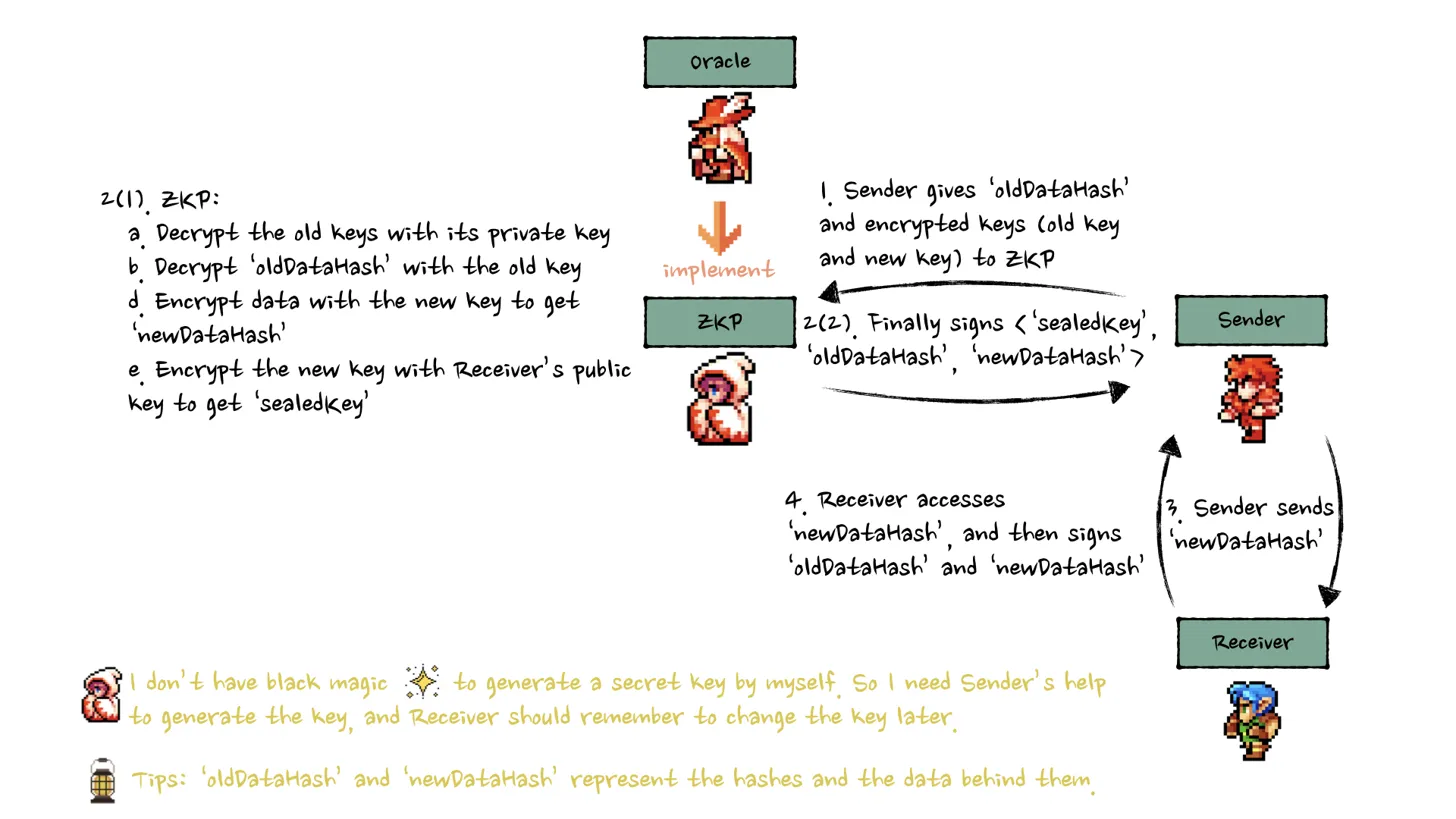
ZKP (Zero-Knowledge Proof)
How it works:
- Sender provides old and new keys to ZKP system
- ZKP circuit verifies correct re-encryption
- Proof generated without revealing keys or data
- Smart contract validates ZKP proof
Considerations:
- Cannot independently generate new keys
- Requires sender to handle key generation
- Receivers should rotate keys post-transfer
- Computationally intensive proof generation
ZKP Circuit Example
// ZKP circuit for verifying re-encryption
use ark_relations::r1cs::SynthesisError;
pub struct ReencryptionCircuit {
// Public inputs (known to verifier)
pub old_data_hash: Option<Fr>,
pub new_data_hash: Option<Fr>,
pub receiver_pubkey: Option<Fr>,
// Private inputs (known only to prover)
pub encrypted_data: Option<Vec<u8>>,
pub old_key: Option<Vec<u8>>,
pub new_key: Option<Vec<u8>>,
pub plaintext_data: Option<Vec<u8>>,
}
impl ConstraintSynthesizer<Fr> for ReencryptionCircuit {
fn generate_constraints(
self,
cs: ConstraintSystemRef<Fr>,
) -> Result<(), SynthesisError> {
// Step 1: Verify decryption of original data
let decrypted = decrypt_constraint(
cs.clone(),
&self.encrypted_data?,
&self.old_key?
)?;
// Step 2: Verify plaintext matches decrypted data
enforce_equal(
cs.clone(),
&decrypted,
&self.plaintext_data?
)?;
// Step 3: Verify re-encryption with new key
let reencrypted = encrypt_constraint(
cs.clone(),
&self.plaintext_data?,
&self.new_key?
)?;
// Step 4: Verify hash consistency
let computed_hash = hash_constraint(cs.clone(), &reencrypted)?;
enforce_equal(
cs,
&computed_hash,
&self.new_data_hash?
)?;
Ok(())
}
}
Implementation Guidelines
Smart Contract Architecture
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/security/ReentrancyGuard.sol";
contract ERC7857 is ERC721, Ownable, ReentrancyGuard {
// State variables
mapping(uint256 => bytes32) private _metadataHashes;
mapping(uint256 => string) private _encryptedURIs;
mapping(uint256 => mapping(address => bytes)) private _authorizations;
// Oracle configuration
address public oracle;
uint256 public constant PROOF_VALIDITY_PERIOD = 1 hours;
// Events
event MetadataUpdated(uint256 indexed tokenId, bytes32 newHash);
event UsageAuthorized(uint256 indexed tokenId, address indexed executor);
event OracleUpdated(address oldOracle, address newOracle);
modifier validProof(bytes calldata proof) {
require(oracle != address(0), "Oracle not set");
require(IOracle(oracle).verifyProof(proof), "Invalid proof");
_;
}
function transfer(
address from,
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
bytes calldata sealedKey,
bytes calldata proof
) external nonReentrant validProof(proof) {
require(ownerOf(tokenId) == from, "Not owner");
require(to != address(0), "Invalid recipient");
// Update metadata access for new owner
_updateMetadataAccess(tokenId, to, sealedKey, proof);
// Transfer NFT ownership
_transfer(from, to, tokenId);
emit MetadataUpdated(tokenId, keccak256(sealedKey));
}
function _updateMetadataAccess(
uint256 tokenId,
address newOwner,
bytes calldata sealedKey,
bytes calldata proof
) internal {
// Verify proof contains correct metadata hash
bytes32 expectedHash = _extractHashFromProof(proof);
_metadataHashes[tokenId] = expectedHash;
// Store new encrypted URI if provided
string memory newURI = _extractURIFromProof(proof);
if (bytes(newURI).length > 0) {
_encryptedURIs[tokenId] = newURI;
}
}
}
Metadata Management
class MetadataManager {
constructor(storageProvider, encryptionService, options = {}) {
this.storage = storageProvider;
this.encryption = encryptionService;
this.options = {
keySize: 256,
algorithm: 'AES-GCM',
...options
};
}
async storeMetadata(data, ownerPublicKey) {
try {
// Validate input data
this._validateMetadata(data);
// Generate encryption key
const key = await this.encryption.generateKey({
size: this.options.keySize,
algorithm: this.options.algorithm
});
// Encrypt metadata
const encrypted = await this.encryption.encrypt(data, key, {
includeMac: true,
version: '1.0'
});
// Store encrypted data on distributed storage
const uri = await this.storage.store(encrypted, {
redundancy: 3,
availability: '99.9%'
});
// Seal key for owner using their public key
const sealedKey = await this.encryption.sealForOwner(
key,
ownerPublicKey
);
// Generate metadata hash for verification
const metadataHash = await this.encryption.hash(encrypted);
return {
uri,
sealedKey,
metadataHash,
algorithm: this.options.algorithm,
version: '1.0'
};
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Metadata storage failed: ${error.message}`);
}
}
async retrieveMetadata(uri, sealedKey, ownerPrivateKey) {
try {
// Fetch encrypted data from storage
const encrypted = await this.storage.retrieve(uri);
// Unseal the encryption key
const key = await this.encryption.unsealKey(
sealedKey,
ownerPrivateKey
);
// Decrypt and return metadata
const decrypted = await this.encryption.decrypt(encrypted, key);
return decrypted;
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Metadata retrieval failed: ${error.message}`);
}
}
_validateMetadata(data) {
if (!data || typeof data !== 'object') {
throw new Error('Invalid metadata format');
}
const maxSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024; // 10MB limit
const serialized = JSON.stringify(data);
if (serialized.length > maxSize) {
throw new Error('Metadata exceeds size limit');
}
}
}
Security Considerations
🔑 Key Management
Best Practices:
- Use hardware security modules (HSM) when available
- Implement automatic key rotation every 90 days
- Store private keys in secure enclaves or hardware wallets
- Never log or expose private keys in error messages
Implementation:
class SecureKeyManager {
constructor(hsmProvider) {
this.hsm = hsmProvider;
this.keyRotationInterval = 90 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000; // 90 days
}
async generateKey() {
// Use HSM if available, fallback to secure random
return this.hsm ?
await this.hsm.generateKey() :
await crypto.subtle.generateKey(/*...*/);;
}
}
🔮 Oracle Security
TEE Verification:
- Always verify TEE attestations before accepting proofs
- Validate enclave signatures and measurement values
- Implement attestation freshness checks
ZKP Auditing:
- Audit circuit implementations thoroughly
- Verify trusted setup parameters
- Test edge cases and malformed inputs
Fallback Mechanisms:
contract OracleManager {
address[] public oracles;
uint256 public minConfirmations = 2;
function verifyWithFallback(bytes calldata proof) external view returns (bool) {
uint256 confirmations = 0;
for (uint i = 0; i < oracles.length; i++) {
if (IOracle(oracles[i]).verifyProof(proof)) {
confirmations++;
}
}
return confirmations >= minConfirmations;
}
}
🛡️ Metadata Privacy
Encryption Standards:
- Use AES-256-GCM for symmetric encryption
- Implement RSA-4096 or ECC-P384 for key sealing
- Always include authentication tags
Storage Security:
- Encrypt metadata before network transmission
- Use 0G Storage for decentralized, tamper-proof storage
- Implement zero-knowledge access controls
Access Patterns:
// Secure metadata access pattern
async function accessMetadata(tokenId, requesterKey) {
// 1. Verify ownership or authorization
const isAuthorized = await verifyAccess(tokenId, requesterKey);
if (!isAuthorized) throw new Error('Unauthorized');
// 2. Retrieve encrypted metadata
const encrypted = await storage.retrieve(getMetadataURI(tokenId));
// 3. Decrypt only if authorized
const decrypted = await decrypt(encrypted, requesterKey);
return decrypted;
}
Advanced Features
Clone Functionality
The clone() function allows creating copies of INFTs while maintaining metadata security:
function clone(
address to,
uint256 tokenId,
bytes calldata sealedKey,
bytes calldata proof
) external returns (uint256) {
require(canClone(tokenId, msg.sender), "Not authorized");
uint256 newTokenId = _mint(to);
_copyMetadata(tokenId, newTokenId, sealedKey, proof);
return newTokenId;
}
Authorized Usage
Enable third parties to use INFT capabilities without ownership:
function authorizeUsage(
uint256 tokenId,
address executor,
bytes calldata permissions
) external {
require(ownerOf(tokenId) == msg.sender, "Not owner");
_authorizations[tokenId][executor] = permissions;
emit UsageAuthorized(tokenId, executor);
}
0G Infrastructure Integration
0G Storage Integration
// Store encrypted AI agent metadata
const metadata = {
model: aiAgent.serializedModel,
weights: aiAgent.trainedWeights,
config: aiAgent.configuration
};
const encrypted = await encryptMetadata(metadata, ownerPublicKey);
const storageResult = await ogStorage.store(encrypted, {
redundancy: 3,
durability: '99.999%'
});
console.log(`Metadata stored at: ${storageResult.uri}`);
0G Compute Integration
// Execute secure inference without exposing model
const inferenceResult = await ogCompute.executeSecure({
tokenId: inftId,
executor: authorizedExecutor,
input: userQuery,
verificationMode: 'TEE' // or 'ZKP'
});
// Result includes proof of correct execution
console.log(`Inference result: ${inferenceResult.output}`);
console.log(`Verification proof: ${inferenceResult.proof}`);
0G Chain Deployment
// Deploy INFT contract to 0G Chain
const ERC7857Factory = await ethers.getContractFactory('ERC7857');
const inftContract = await ERC7857Factory.deploy(
'AI Agent NFTs',
'AINFT',
oracleAddress,
ogStorageAddress
);
await inftContract.deployed();
console.log(`INFT contract deployed at: ${inftContract.address}`);
Resources & References
Official Documentation
📜 EIP-7857 Specification - Official Ethereum standard proposal
💻 Reference Implementation - Complete codebase with examples
🔒 Security Audit Reports - Third-party security assessments (coming soon)
Community & Support
💬 Developer Forum - Technical discussions and Q&A
🐛 GitHub Issues - Bug reports and feature requests
📚 Knowledge Base - Common implementation patterns
Standards & Specifications
📄 ERC-721 Standard - Base NFT standard
🔐 Encryption Standards - NIST cryptography guidelines
🛡️ TEE Specifications - Intel SGX documentation
Next Steps
For Implementation
🚀 Integration Guide - Step-by-step development guide
🎯 Use Cases - Real-world implementation examples
📋 Best Practices Guide - Production deployment guidelines (coming soon)
For Testing
🧪 Testnet Deployment - Test your implementation
🗗️ Oracle Testing - Verify TEE and ZKP implementations
🔍 Security Testing - Audit your contracts
Community
💬 Join Discussions - Share implementations and get feedback
🚀 Contribute - Help improve the standard and tooling
📚 Learn - Explore advanced features and optimizations