0G DA: Infinitely Scalable and Programmable DA
The Rise of Data Availability Layers
Data availability (DA) refers to proving that data is readily accessible, verifiable, and retrievable. For example, Layer 2 rollups such as Arbitrum or Base reduce the burden from Ethereum by handling transactions off-chain and then publishing the data back to Ethereum, thereby freeing up L1 Ethereum throughput and reducing gas. The transaction data, however, still needs to be made available so that anyone can validate or challenge the transactions through fraud-proofs during the challenge-period.
As such, DA is crucial to blockchains as it allows for full validation of the blockchain's history and current state by any participant, thus maintaining the decentralized and trustless nature of the network. Without this, validators would not be able to independently verify the legitimacy of transactions and blocks, leading to potential issues like fraud or censorship.
This led to the arrival of Data Availability Layers (DALs), which provide a significantly more efficient manner of storing and verifying data than publishing directly to Ethereum. DALs are critical for several reasons:
- Scalability: DALs allow networks to process more transactions and larger datasets without overwhelming the system, reducing the burden on network nodes and significantly enhancing network scalability.
- Increased Efficiencies: DALs optimize how and where data is stored and made available, increasing data throughput and reducing latency while also minimizing associated costs.
- Interoperability & Innovation: DALs that can interact with multiple ecosystems allow for fast and highly secure interoperability for data and assets.
However, it's worth noting that not all DALs are built equally.
The Challenge Today
Existing DALs tend to require that data be simultaneously sent to all of their network nodes, preventing horizontal scalability and limiting network speed to its slowest node. They also do not have built-in storage systems, requiring connectivity to external systems that impact throughput, latency, and cost.
Additionally, 0G inherits Ethereum's security, while other systems rely upon their own security mechanisms that fall short. This is significant because Ethereum's network is secured by over 34 million ETH staked, representing approximately $80 billion in cryptoeconomic security at the time of writing. In contrast, competitors rely on security mechanisms that, at best, represent only a fraction of Ethereum's total security. This gives 0G a distinct advantage, as it leverages the vast economic incentives and decentralization of Ethereum's staking system, providing a level of protection that competitors cannot match.
Even more issues exist, including EigenDA's lack of randomization over its data committees. As data committees are core to a DA system's integrity, a lack of randomization means that collusion is theoretically possible for malicious nodes to predict when they might be on a committee together.
0G's core differentiation is massive throughput and scalability.
This is possible through 0G's unique design includes a built-in storage system and horizontally scalable consensus design, alongside other clever design mechanisms that we'll cover below.
The result is that 0G serves as the foundational layer for decentralized AI applications, bringing on-chain AI and more to life.
Why 0G
There are 4 differentiators of 0G worth highlighting:
-
Infinitely Scalable DA: 0G's infinitely scalable DAL can quickly query or confirm data as valid, whether data is held by 0G Storage, or external Web2 or Web3 databases. Infinite scalability comes from the ability to continuously add new consensus networks, supporting workloads that far surpass the capacity of existing systems.
-
Modular and Layered Architecture: 0G's design decouples storage, data availability, and consensus, allowing each component to be optimized for its specific function. Data availability is ensured through redundancy, with data distributed across decentralized Storage Nodes. Cryptographic proofs (like Merkle trees and zk-proofs) verify data integrity at regular intervals, automatically replacing nodes that fail to produce valid proofs. And combined with 0G's ability to keep adding new consensus networks that scale with demand, 0G can scale efficiently and is ideal for complex AI workflows and large-scale data processing.
-
Decentralized AI Operating System & High Throughput: 0G is the first decentralized AI operating system (dAIOS) designed to give users control over their data, while providing the infrastructure necessary to handle the massive throughput demands of AI applications. Beyond its modular architecture and infinite consensus layers, 0G achieves high throughput through parallel data processing, enabled by erasure coding, horizontally scalable consensus networks, and more. With a demonstrated throughput of 50 Gbps on the Newton Testnet, 0G seamlessly supports AI workloads and other high-performance needs, including training large language models and managing AI agent networks.
These differentiators make 0G uniquely positioned to tackle the challenges of scaling AI on a decentralized platform, which is critical for the future of Web3 and decentralized intelligence.
How Does This Work?
As covered in #0G_Storage, data within the 0G ecosystem is first erasure-coded and split into "data chunks," which are then distributed across various Storage Nodes in the 0G Storage network.
To ensure data availability, 0G uses Data Availability Nodes that are randomly chosen using a Verifiable Random Function (VRF). A VRF generates random values in a way that is unpredictable yet verifiable by others, which is important as it prevents potentially malicious nodes from collusion.
These DA nodes work together in small groups, called quorums, to check and verify the stored data. The system assumes that most nodes in each group will act honestly, known as an "honest majority" assumption.
The consensus mechanism used by 0G is fast and efficient due to its sampling-based approach. Rather than verifying all data, DA nodes sample portions of it, drastically reducing the data they need to handle. Once enough nodes agree that the sampled data is available and correct, they submit availability proofs to the 0G Consensus network. This lightweight, sample-driven approach enables faster verification while maintaining strong security.
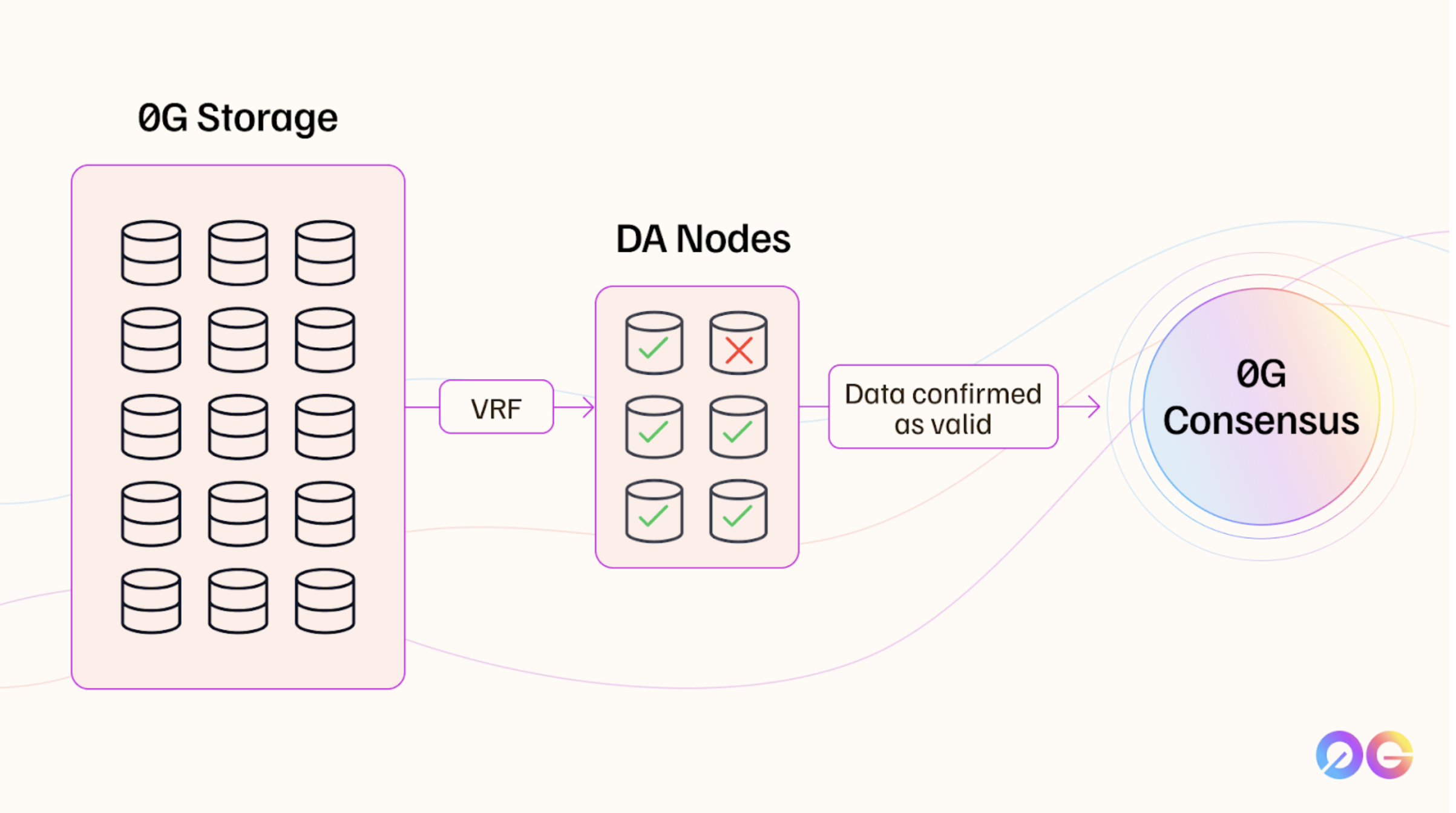
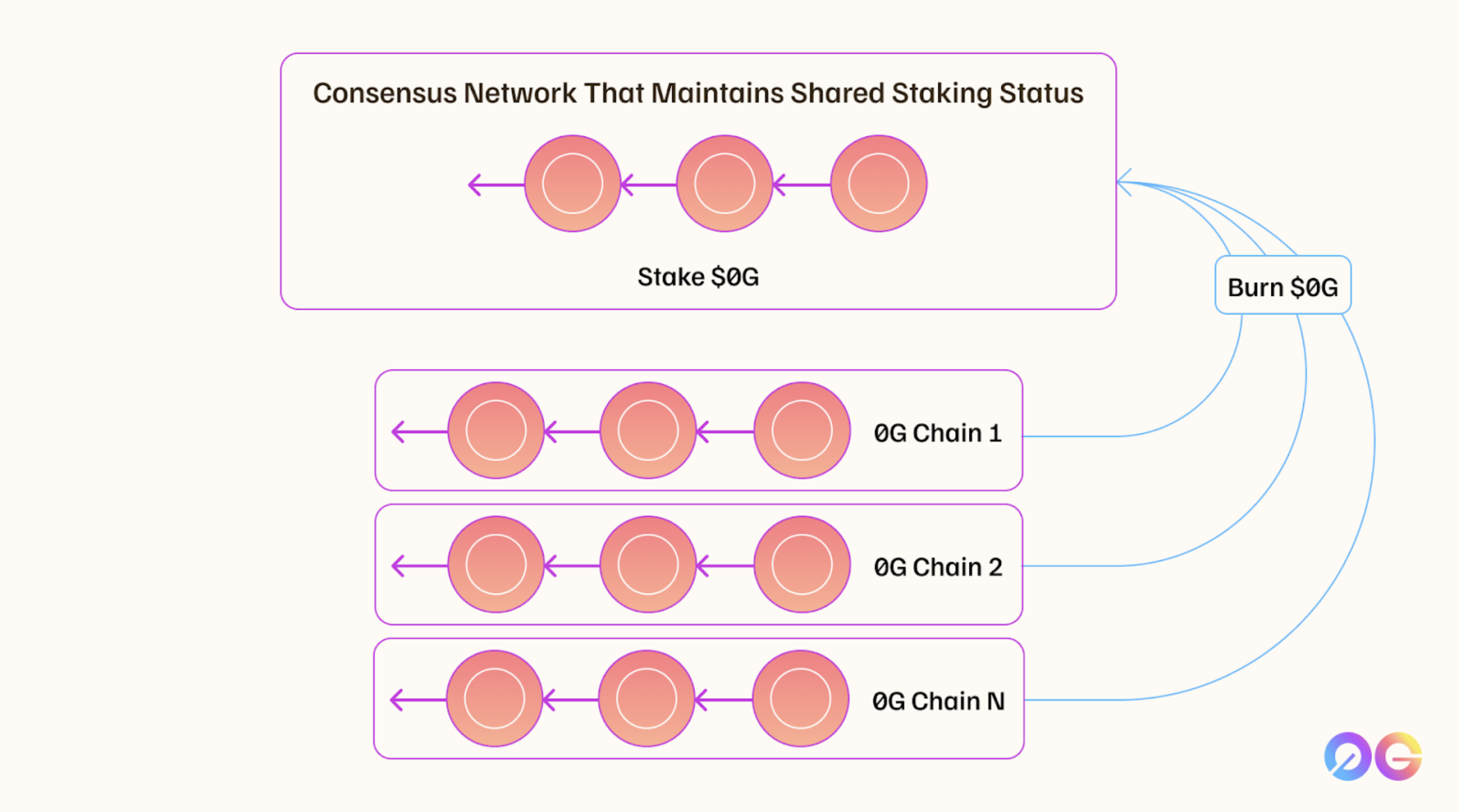
Validators in the 0G Consensus network, who are separate from the DA nodes, verify and finalize these proofs. Although DA nodes ensure data availability, they do not directly participate in the final consensus process, which is the responsibility of 0G validators. Validators use a shared staking mechanism where they stake $0G tokens on a primary network (likely Ethereum). Any slashable event across connected networks leads to slashing on the main network, securing the system's scalability while maintaining robust security.
This is a key mechanism that allows for the system to scale infinitely while maintaining data availability. In return, validators engaged in shared staking receive 0G tokens on the mainnet.
Getting started: link to guide
Use Cases
0G DA offers an infinitely scalable and high-performance DA solution for a wide range of applications across Web3, AI, and more.
L1s / L2s
Layer 1 and Layer 2 chains can utilize 0G DA to handle data availability and storage requirements for decentralized AI models, large datasets, and on-chain applications. Existing partners include networks like Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, Fuel, Manta Network, and countless more, which leverage 0G's scalable infrastructure to store data more efficiently and support fast retrieval.
Decentralized Shared Sequencers
Decentralized Shared Sequencers help order L2 transactions before final settlement on Ethereum. By integrating 0G DA, shared sequencers can streamline data across multiple networks in a decentralized manner, unlike existing sequencers which are often centralized. This also means fast and secure data transfers between L2s.
Bridges
Cross-chain bridges benefit from 0G DA's scalable storage and data availability features. Networks can store and retrieve state data using 0G DA, making state migration between networks faster and more secure. For example, a network can confirm a user's assets and transfer them securely to another chain using 0G's highly efficient data verification.
Rollups-as-a-Service (RaaS)
0G DA can serve as a reliable DA solution for RaaS providers like Caldera and AltLayer, enabling seamless configuration and deployment of rollups. With 0G DA's highly scalable infrastructure, RaaS providers can ensure the secure availability of data across multiple rollups without compromising performance.
DeFi
0G's DA infrastructure is ideally suited for DeFi applications that require fast settlement and high-frequency trading. For example, by storing order book data on 0G, DeFi projects can achieve faster transaction throughput and enhanced scalability across L2s and L3s.
On-Chain Gaming
On-chain gaming platforms rely on cryptographic proofs and metadata related to player assets, actions, and scores. 0G DA's ability to handle large volumes of data securely and efficiently makes it an optimal solution for gaming applications that require reliable data storage and fast retrieval.
Data Markets
Web3 data markets can benefit from 0G DA by storing datasets on-chain. The decentralized storage and retrieval capabilities of 0G enable real-time updates and querying of data, providing a reliable solution for data market platforms.
AI & Machine Learning
0G DA is particularly focused on supporting decentralized AI, allowing full AI models and vast datasets to be stored and accessed on-chain. This infrastructure is essential for advanced AI applications that demand high data throughput and availability, such as training large language models (LLMs) and managing entire AI agent Networks.