0G Storage: Built for Massive Data
Intro to Storage Systems
Storage systems play a critical role in managing, organizing, and ensuring the accessibility of data. In traditional systems, data is often stored centrally, creating risks around availability, censorship, and data loss due to single points of failure. Decentralized storage, on the other hand, addresses these issues by distributing data across a network of nodes, enhancing security, resilience, and scalability. This decentralization is essential, especially in an era where massive data sets are generated and consumed by AI, Web3 applications, and large-scale businesses.
0G's Storage System
0G Storage is a distributed data storage system designed with on-chain elements to incentivize storage nodes to store data on behalf of a user. Anyone can run a storage node and receive rewards for maintaining one. For information on how to do so, check out our guide here.
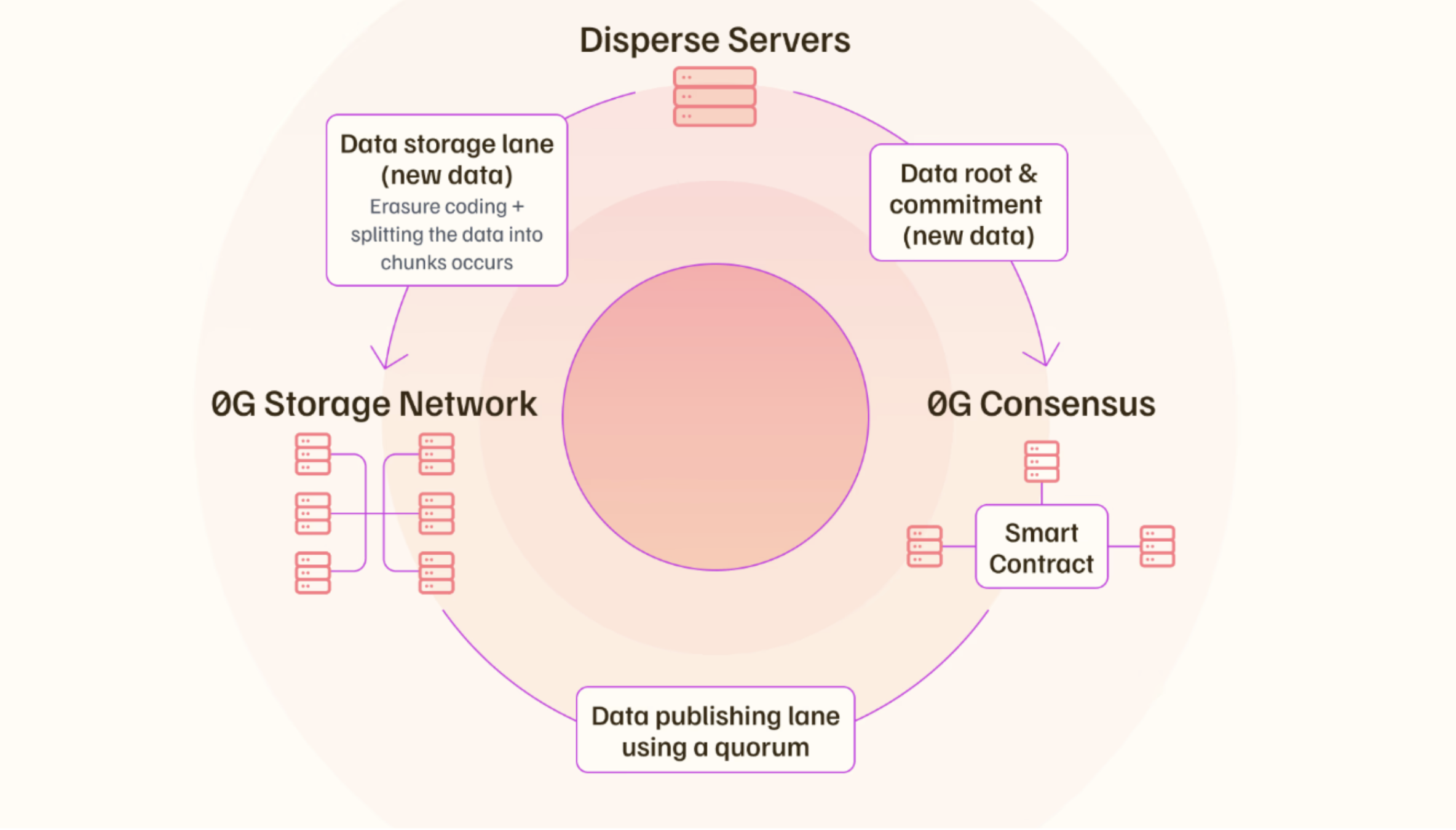
0G's system itself has two parts:
- The Data Publishing Lane: Ensures data availability by allowing quick queries and verification through the 0G Consensus network. This ensures that the data stored can be easily accessed and validated by users or applications when needed.
- The Data Storage Lane: Manages large data transfers and storage, utilizing an erasure-coding mechanism. This splits data into smaller, redundant fragments distributed across different nodes, guaranteeing data recovery in case of node failure or downtime.
For any party wishing to store data with 0G, the data must first be provided alongside payment using 0G's token, which is fully embedded into 0G's main chain. To store this data, it is first erasure-coded, meaning that the data being stored is fragmented into redundant smaller pieces distributed across multiple storage locations. Redundancy is essential as it ensures the data can always be recovered, even if some storage locations fail or become unavailable.
0G system also has "disperse servers" that handle:
- Erasure coding the data and distributing it across multiple storage nodes.
- Generating a data root, which is essentially the Merkle root of the encoded data chunks. This root serves as a commitment to the integrity and completeness of the data. A Merkle root is a cryptographic hash that is formed by combining hashes from various individual transactions.
0G's storage infrastructure is designed to support heavy data loads, making it a strong candidate for applications that demand high throughput and reliability. With separate consensus networks managing distinct storage partitions (covered in #0G_CHAIN), 0G's storage system scales effortlessly, addressing the needs of users with data needs of any size.
The 0G Storage Architecture
0G Storage is built on a layered architecture designed to accommodate both unstructured and structured data, ensuring flexibility and scalability for a wide range of applications.
- The Log Layer: Handles unstructured data and functions similarly to a traditional computer file system. This layer is ideal for storing large-scale data storage where the data does not change (e.g. archival purposes, data logs) as it is an append-only system, meaning new data can be added but not modified.
- The Key-Value (KV) Layer: Built on top of the Log Layer, the Key-Value Layer is optimized for structured data. Unlike the log layer, this layer is mutable and can be updated via new entries that are added to log entries, allowing for efficient storage and retrieval of key-value pairs. This layer is best for dynamic applications that require frequent updates, such as databases or collaborative documents (e.g. an on-chain version of Notion or Google Docs).
Both layers are secured and validated through 0G's Consensus, which guarantees the accuracy and availability of all stored data.
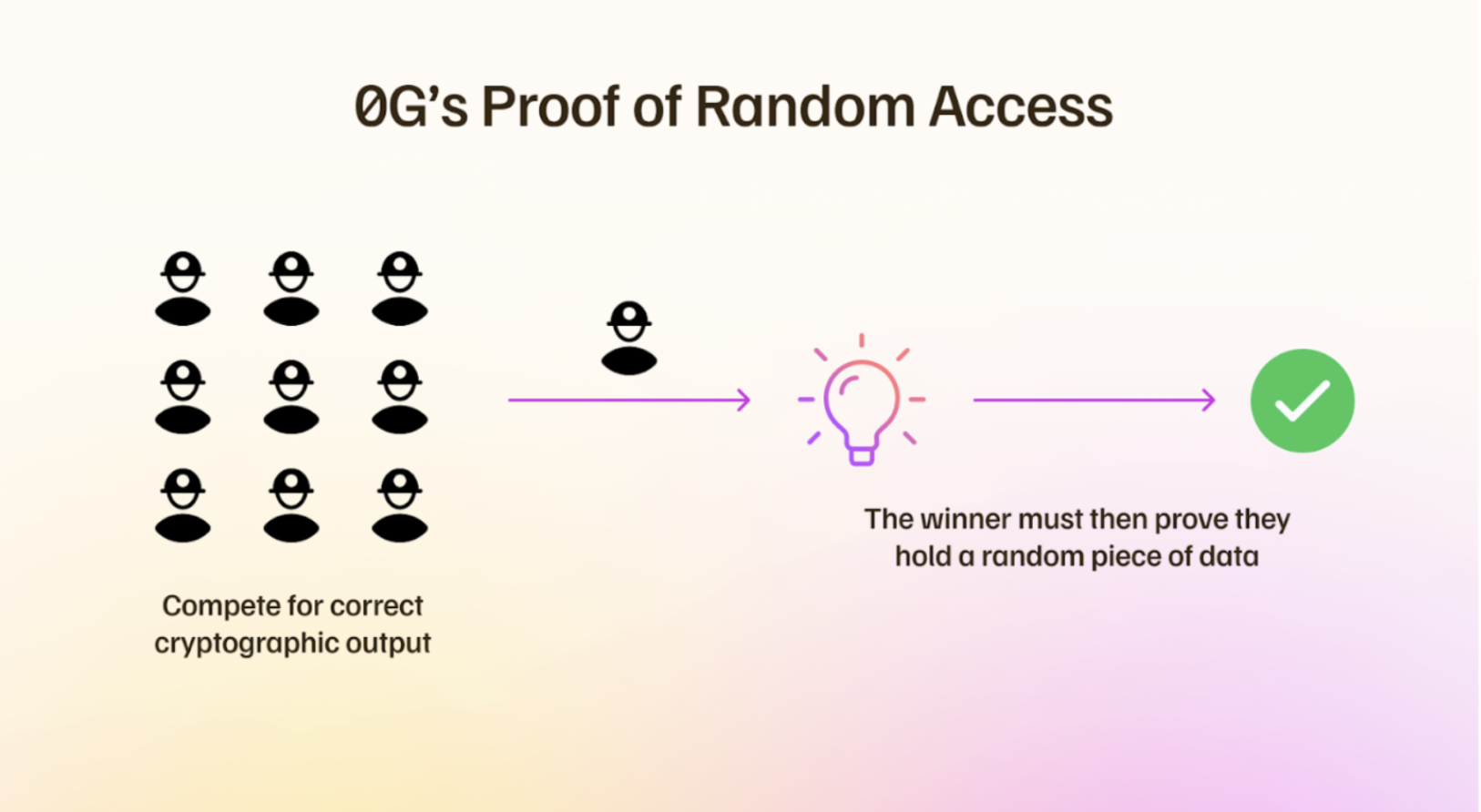
Proof of Random Access
0G Storage is maintained by a network of miners incentivized to store and manage data through a unique consensus mechanism known as Proof of Random Access (PoRA).
Miners are periodically challenged to confirm that they are actively storing specific data chunks. This process works similarly to Proof of Work (PoW), where miners must provide a valid cryptographic hash to verify they are storing the correct data. Before a miner can respond to a query, they must be selected by generating a satisfactory cryptographic output: typically, a hash with a certain number of leading zeros.
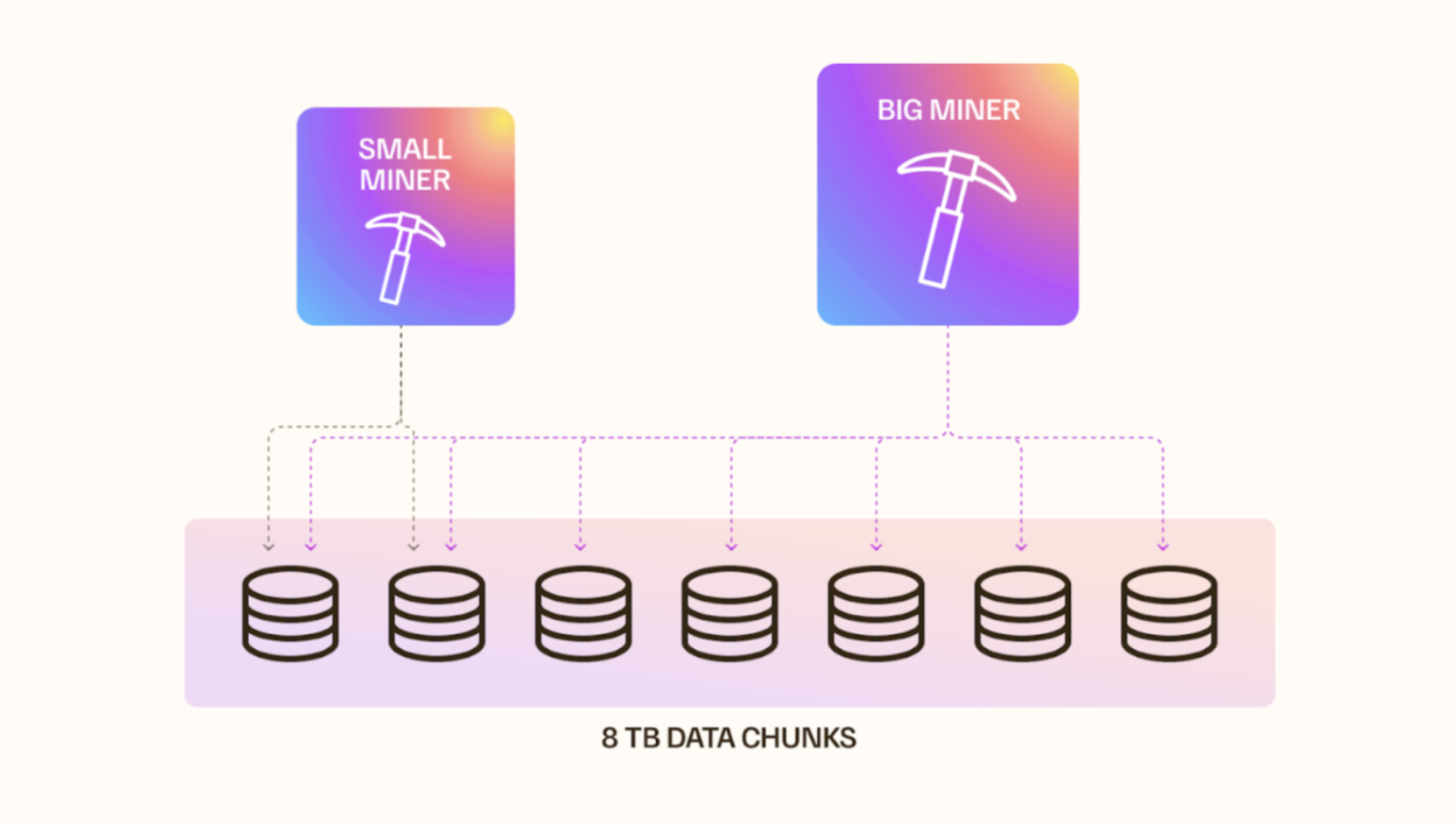
To promote fairness, the mining range is capped at 8 TB of data per mining operation. This ensures that smaller-scale miners with fewer machines can compete on an even playing field with larger operators.
Miners with more resources can still participate by dividing their machines across multiple 8 TB ranges, allowing them to mine simultaneously in various data segments. Meanwhile, smaller miners can focus on a single 8 TB range, ensuring that the process remains competitive and inclusive for all participants, regardless of scale.
Comparison to Filecoin and Arweave
Decentralized storage systems like Filecoin and Arweave face significant limitations surrounding structured data, scalability, cost, and data availability functionality.
These can be summarized as follows:
- Unstructured Data Only: Both of these systems are optimized only for unstructured data, limiting their versatility. In contrast, 0G supports both structured and unstructured data, making it suitable for a wider range of applications, including complex AI workflows and their vast databases.
- Scalability: Filecoin or Arweave struggle to handle data at a massive scale. In contrast, 0G partitions both its data storage and network throughput to enable scalability that meets the massive data requirements associated with on-chain AI.
- Cost: Benchmarking has shown that permanent storage with Arweave can cost up to $17,000 per TB, while 0G offers a much more cost-effective solution at just $10-11 per TB.
- Data Availability: 0G's integrated data availability layer provides ultra-fast, infinitely scalable access to data, enabling a fully vertically integrated solution that supports high-performance applications like decentralized AI.
All in all, 0G Storage is the ultimate solution for any on-chain data storage needs, regardless of whether a project is in the AI space or not.