INFTs: Tokenizing AI Agents
The rapid growth of AI agents necessitates new methods for managing their ownership, transfer, and capabilities within Web3 ecosystems. INFTs (Intelligent Non-Fungible Tokens) represent a significant advancement in this space, enabling the tokenization of AI agents to provide transferability, decentralized control, full asset ownership, and royalty potential.
Challenges with Existing NFT Standards
Traditional NFT standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155 have significant limitations when applied to AI agents, particularly concerning the handling of their unique and often sensitive "intelligence" or metadata:
- Static and Public Metadata: Existing standards typically link to static, publicly accessible metadata (e.g., a URI pointing to a JSON file). AI agents, however, require dynamic metadata that reflects their learning and evolution, and this data often needs privacy protection.
- Insecure Metadata Transfer: When transferring an ERC-721 token, only the ownership identifier moves—not the underlying metadata. For AI agents, this means the new owner might receive an incomplete or non-functional agent.
- Lack of Native Encryption/Privacy: Current standards don't inherently support the encryption needed to protect proprietary AI models or sensitive user data contained within an agent's metadata.
ERC-7857: A Standard Designed for AI Agents
ERC-7857 is a new NFT standard introduced by 0G Labs, specifically designed to address these shortcomings. It enables the creation, ownership, and secure transfer of INFTs with their complete intelligence intact.
Key Features & Advantages
- Privacy-Preserving Metadata: Allows sensitive metadata (the agent's "intelligence") to be encrypted and kept private, protecting proprietary information.
- Secure Metadata Transfers: Ensures that when an INFT is transferred, both the ownership and the encrypted metadata are securely passed to the new owner in a verifiable way.
- Dynamic Data Management: Supports the dynamic nature of AI agents, allowing their metadata (state, models, behaviors) to be updated securely within the NFT framework.
- Decentralized Storage Integration: Works with systems like 0G Storage for secure, permanent, and tamper-proof storage and access management of metadata.
- Verifiable Ownership & Control: Uses cryptographic proofs and oracles to validate metadata transfers, ensuring integrity.
- AI-Specific Functionality: Built for AI use cases, enabling features like agent lifecycle management and ownership verification before task execution.
How ERC-7857 Works
The transfer mechanism in ERC-7857 is designed to ensure that both token ownership and access to the token's encrypted metadata are securely transferred. This process involves several key components:
Core Process Flow
- Encryption & Commitment: The AI agent's metadata is encrypted. A hash (commitment) of this encrypted data is created as proof of authenticity without revealing the content.
- Secure Transfer Initiation: When the INFT is transferred, a trusted oracle (potentially using secure environments like TEEs) decrypts the original metadata.
- Re-encryption for Receiver: The oracle generates a new encryption key, re-encrypts the metadata with it, and stores this new encrypted metadata (e.g., on 0G Storage).
- Key Delivery: The new encryption key is encrypted using the receiver's public key. This ensures only the intended new owner can access the actual metadata key.
- Verification & Finalization: The transfer function on the smart contract verifies proofs: the sender's access, the oracle's validation that the new metadata matches the old, and the receiver's signed acknowledgment. If valid, the NFT ownership transfers, and the receiver gets the encrypted metadata key.
- Access Granted: The receiver uses their private key to decrypt the metadata key, granting them full access to the agent's encrypted intelligence.
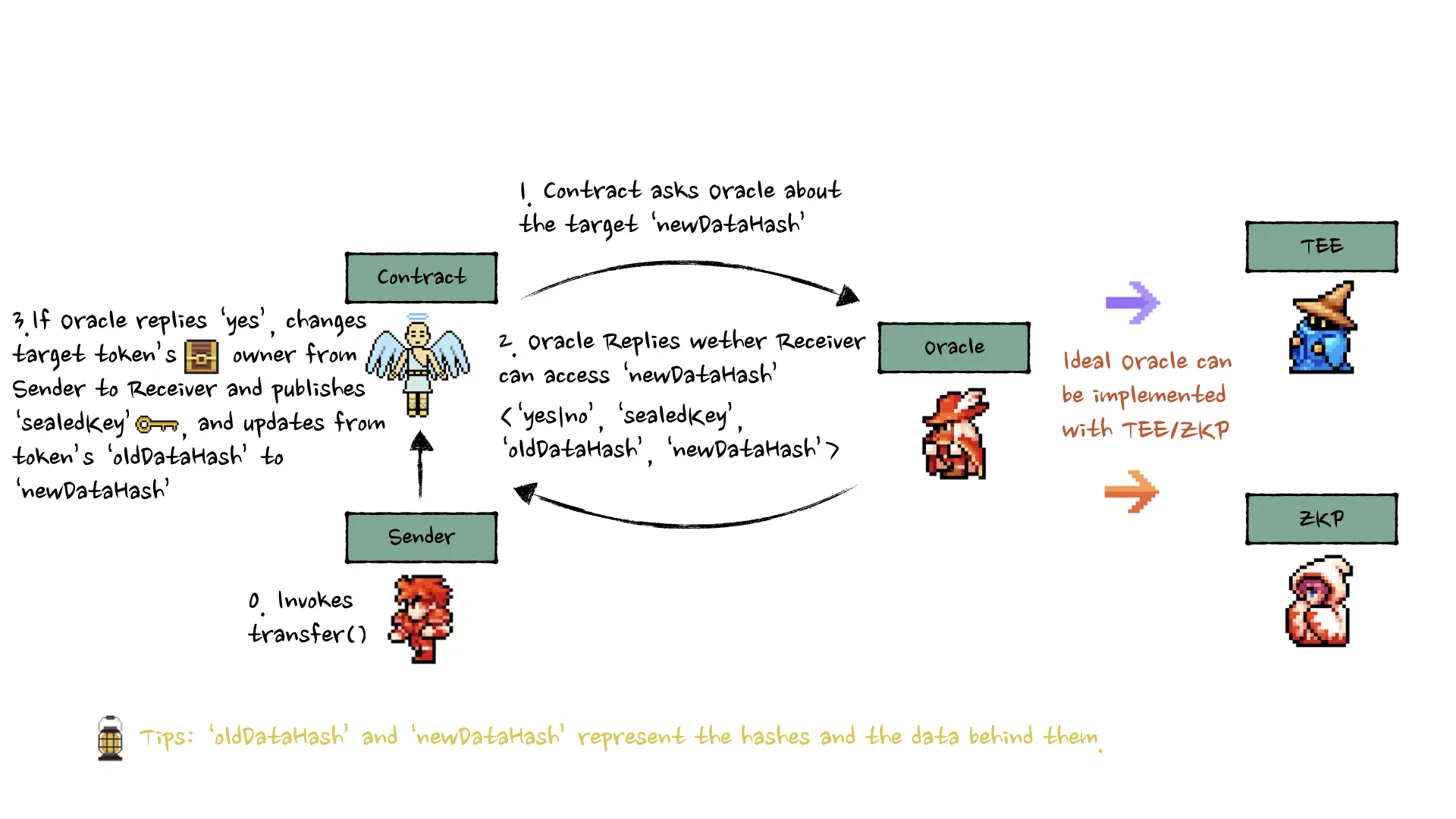
Oracle Implementations
ERC-7857 supports two primary oracle implementations:
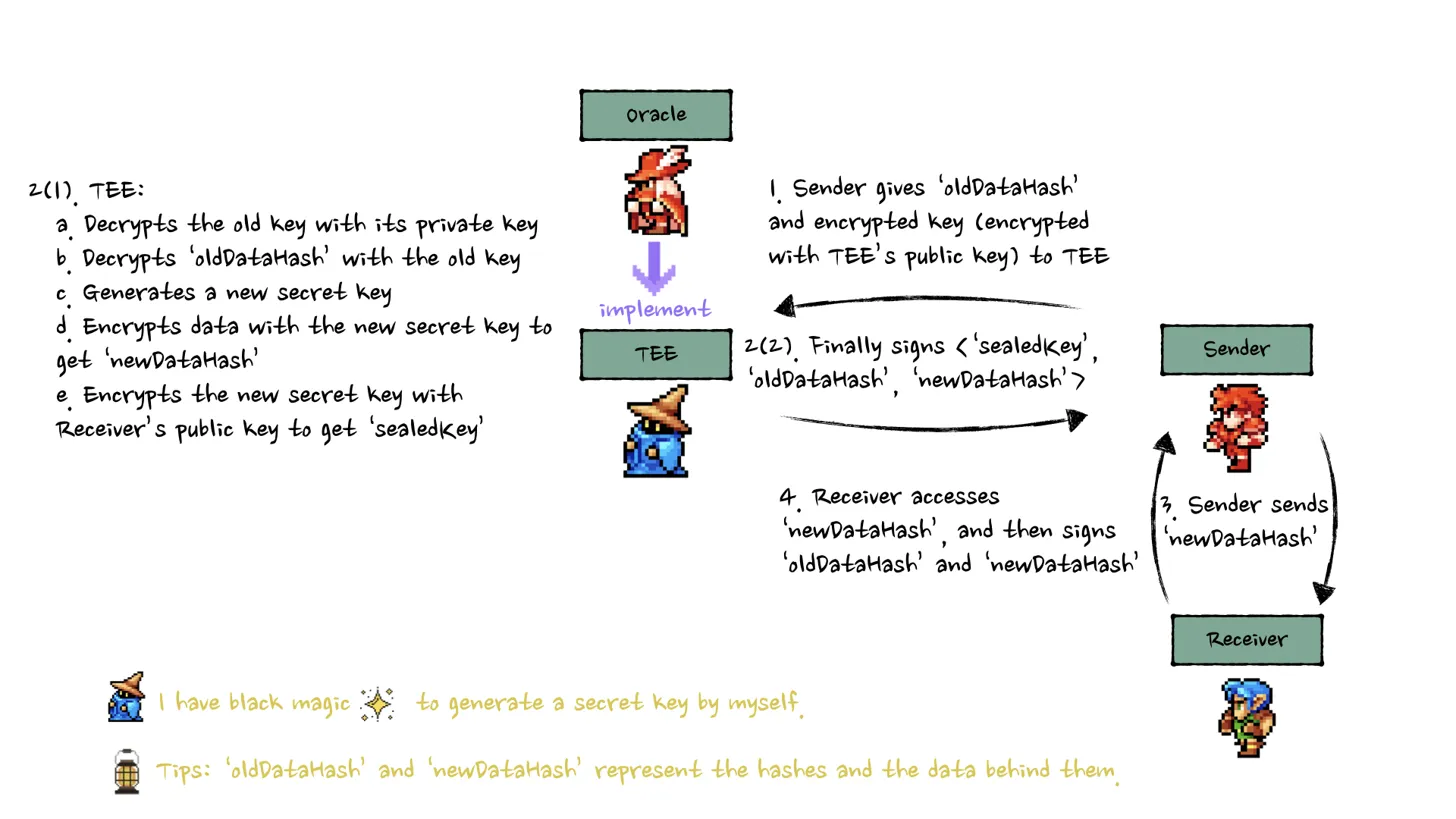
TEE (Trusted Execution Environment)
In the TEE implementation:
- The sender transmits the encrypted data and key to the TEE
- The TEE securely decrypts the data, generates a new key, and re-encrypts the metadata
- The TEE encrypts the new key with the receiver's public key
- The TEE outputs the sealed key and corresponding hash values
- This approach offers strong security as the TEE can generate its own secure keys
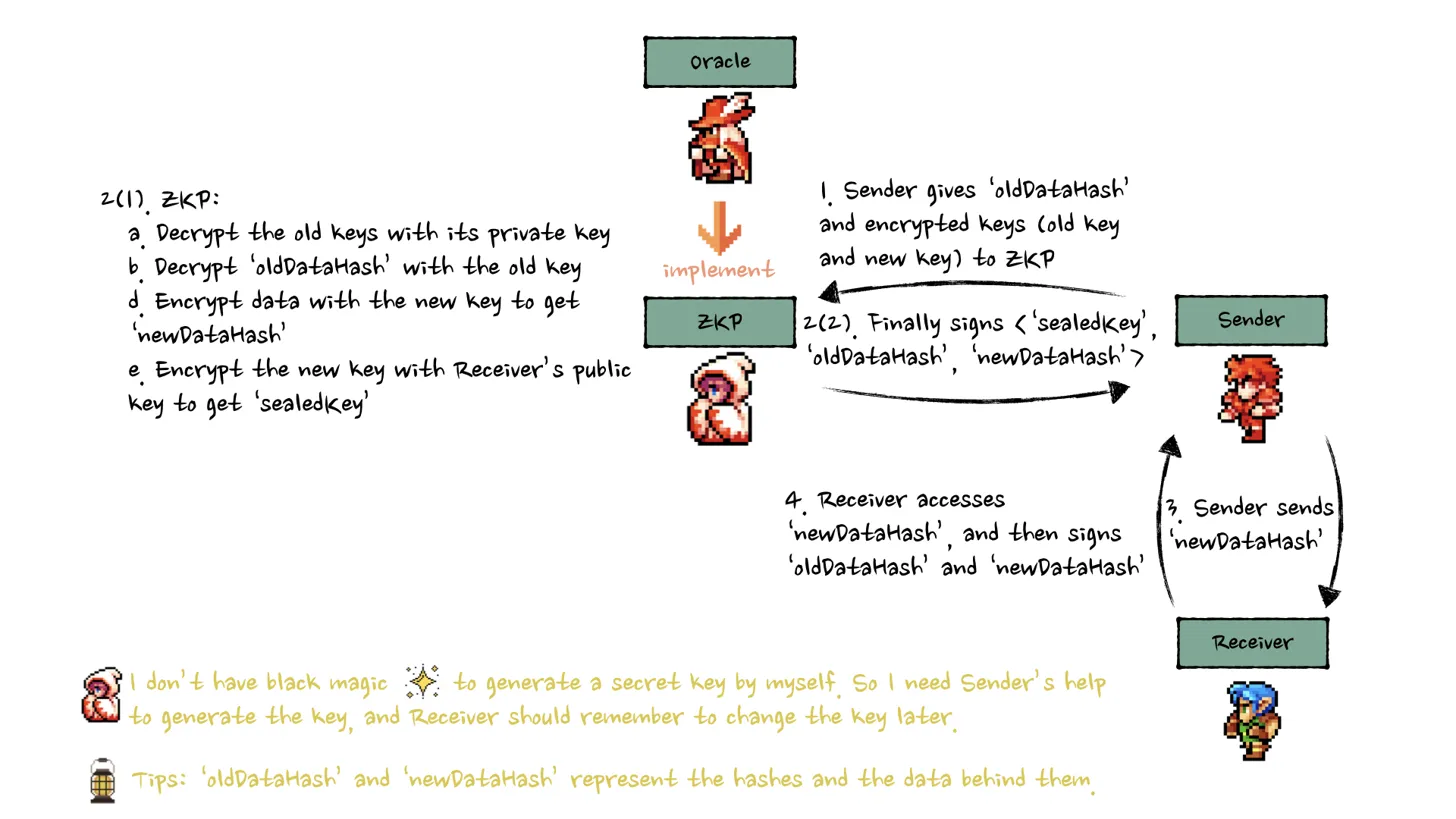
ZKP (Zero-Knowledge Proof)
In the ZKP implementation:
- The sender provides both old and new keys to the ZKP system
- The ZKP verifies that the metadata was correctly re-encrypted
- Unlike TEE, ZKP cannot independently generate new keys
- Receivers should change keys after transfer for enhanced security
Additional Functions
ERC-7857 also supports:
- clone(): Similar to transfer() but creates a new token with the same metadata instead of changing ownership of the original token.
- authorizeUsage(): Adds authority for using the token's private metadata without granting access to the raw data, requiring a sealed executor that processes the metadata securely.
Applications and Use Cases
The ability to securely tokenize and transfer AI agents opens up numerous possibilities:
- AI Agent Marketplaces: Platforms for buying and selling trained AI agents, with guaranteed secure transfer of their capabilities.
- Personalized Automation: Owning and trading INFTs tailored for specific tasks (e.g., DeFi operations, airdrop claiming).
- Enterprise AI Solutions: Building, owning, and securely transferring or leasing proprietary AI agents for internal or client use.
- AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS): Tokenizing and leasing AI agents on subscription models.
- Agent Collaboration: Combining or composing different INFT agents to create more powerful tools.
- Intellectual Property Monetization: Allowing AI developers to monetize their models as NFTs while controlling usage.
Integration with 0G Infrastructure
INFTs leverage the 0G ecosystem in several key ways:
- 0G Storage: Provides the secure, decentralized storage layer required for encrypted metadata, ensuring it remains accessible only to legitimate owners.
- 0G DA (Data Availability): Guarantees the verified availability of metadata proofs necessary for the transfer verification process.
- 0G Chain: Enables fast, scalable execution of INFT operations at lower cost than existing solutions.
- 0G Compute Network: Can be utilized by INFTs for performing secure inferences, enabling AI agents to execute tasks without exposing their underlying model.
By combining INFTs with 0G's comprehensive AI infrastructure, developers can create sophisticated, transferable AI agents that maintain their intelligence, privacy, and functionality throughout their lifecycle.
Getting Started
To begin working with INFTs on the 0G ecosystem, developers can reference our GitHub repository for sample implementations and integration examples. The ERC-7857 standard is designed to be compatible with existing Web3 infrastructure while providing the enhanced security and functionality needed for AI agent tokenization.